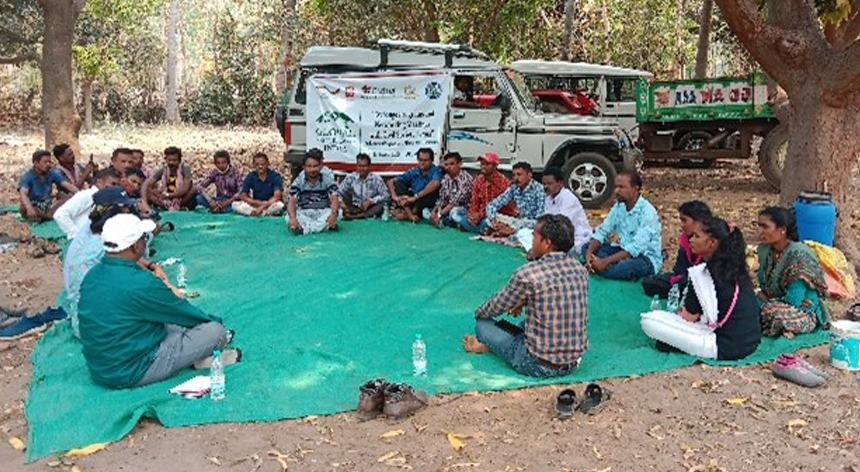
Caritas India joins hands with Odisha Professional Development Consultant Services (OPDCS), one of the nodal NGOs of Odisha Millet Mission for Rayagada and Bissum Cuttack Block for the promotion of millet in the area. International Year of Millets 2023 is a great opportunity for Caritas India and its implementing partner SWAD-Rayagada in Odisha to promote millet cultivation and consumption to improve Nutrition and Food Security among the target communities in the Global Program areas. As a first step, Caritas India organized an "Exchange Programme and Networking Meeting of Civil Society Actors" in the operational areas of OPDSC, Rayagada on 14-15 March 2023.
Author: GlobalIndia (GlobalIndia )
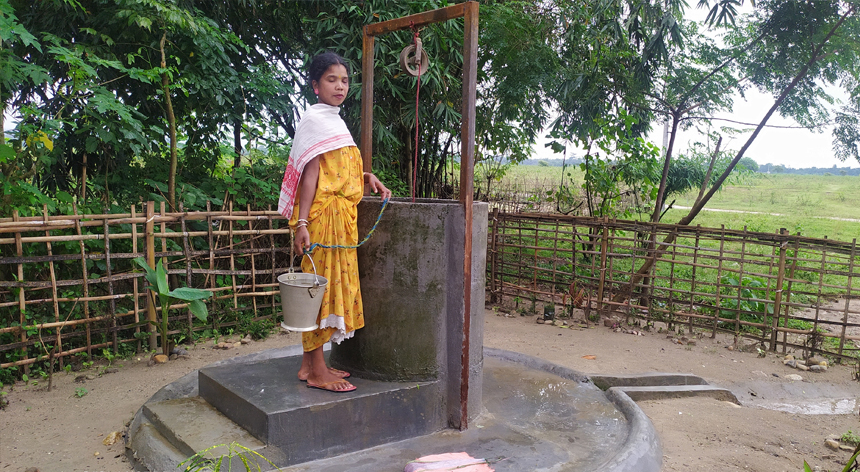

Resilient infrastructure ensures access to safe drinking water even during floods
Hundreds of residents from 13/10 grant villages in Lakhimpur, Assam, now have year-round access to clean drinking water, even during floods. The villagers suffer due to the annual flooding brought on by the early monsoon rains in the months of May–September, which destroys all the water sources. The village is divided into 3 hamlets, where one hamlet is completely deprived of clean water.
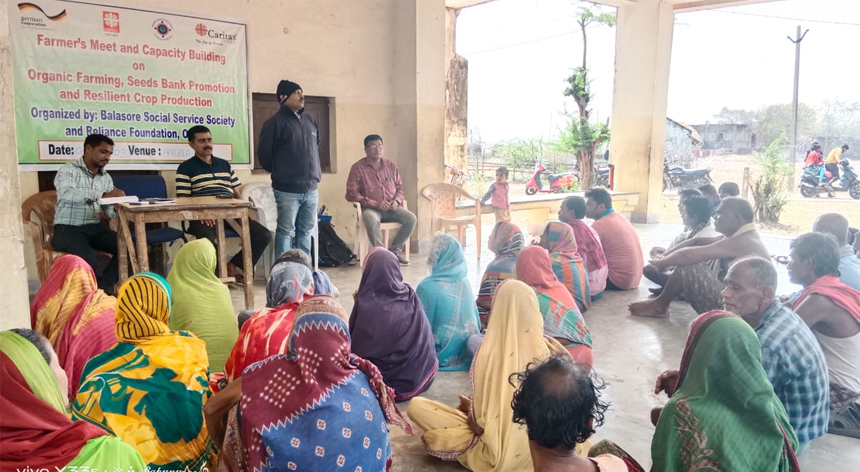

Climate adaptive livelihood solutions bring community resilience
Improving the lives of the particularly marginalized population through ensuring food security and building resilience to natural disasters is the key component of Global program India. Smallholder farmers living in the Odisha coast are vulnerable to socioeconomic and environmental challenges and have little power to seize any opportunity to overcome their situation. The people of Andola and Balimeda, situated near the Mantei River in Bhadrak, are poorly affected by salinity and struggle to cope. The river’s saline water mixes with groundwater and reservoirs and affects agriculture.
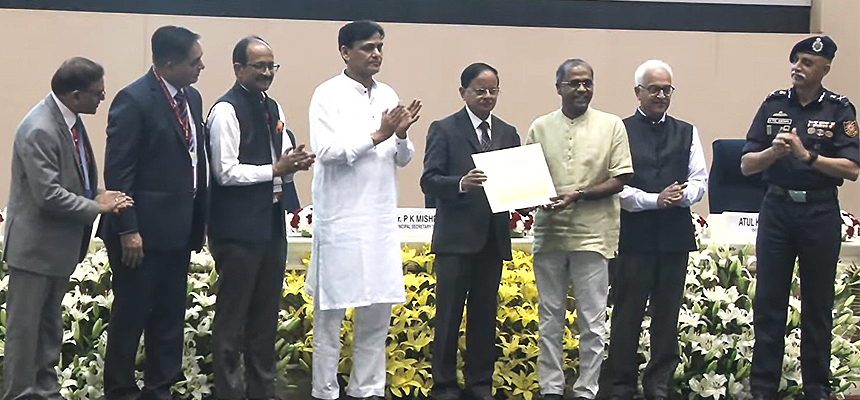
Caritas India Global Program wins the second prize for the Community Early Warning System in the short film competition at the 3rd session of #NPDRR held on 11 March 2023. Fr. (Dr.) Paul Moonjely, Executive Director received the award from Dr. P.K. Mishra, Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister of India.

Global Program’s DRR models exhibited in the G20 summit- NPDRR Side Event on Strengthening Social Protection Systems
National Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction (NPDRR) has been constituted by Government of India with an aim to develop a comprehensive Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) apparatus at national and district level. To ease the integration of disaster management into developmental planning in many sectors and at all levels, from the national to the local, there is a need to establish an environment that is conducive to the creation of a culture of prevention and to enable concerted efforts.
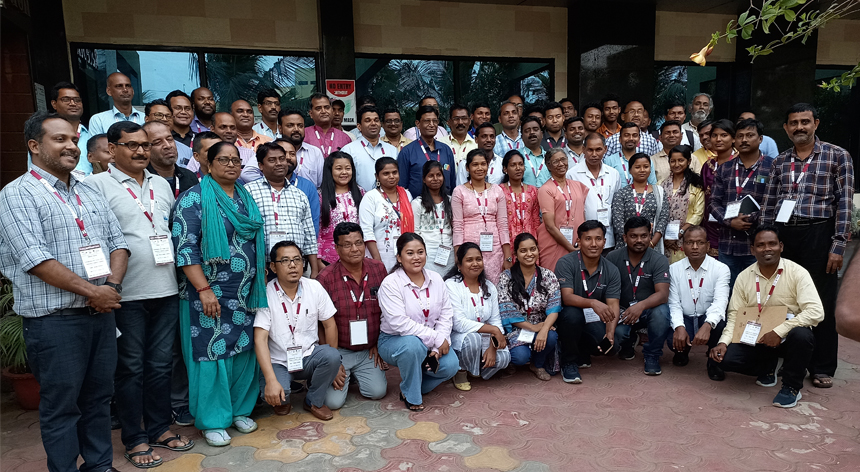

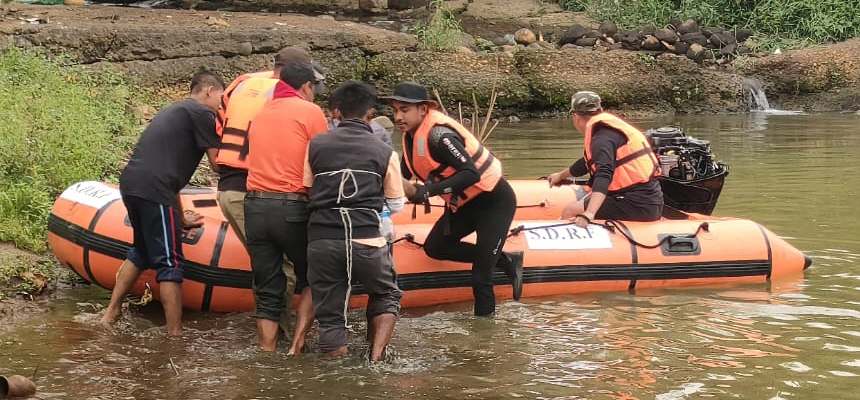
Technical training essential to improve disaster risk resilience
The frequency of disasters in the country has created a pertinent need for proactive and skilled humanitarian workers in the field. Climate change accelerated the intensity of natural hazards and pushed hundreds and thousands of people into abject poverty. As the nature and magnitude of the disasters are ever-evolving, so is the need for effective responses in different geographies. To face this challenge, Caritas India works with the community and stakeholders at different levels to identify, prepare for, respond to, and recover from natural hazards.
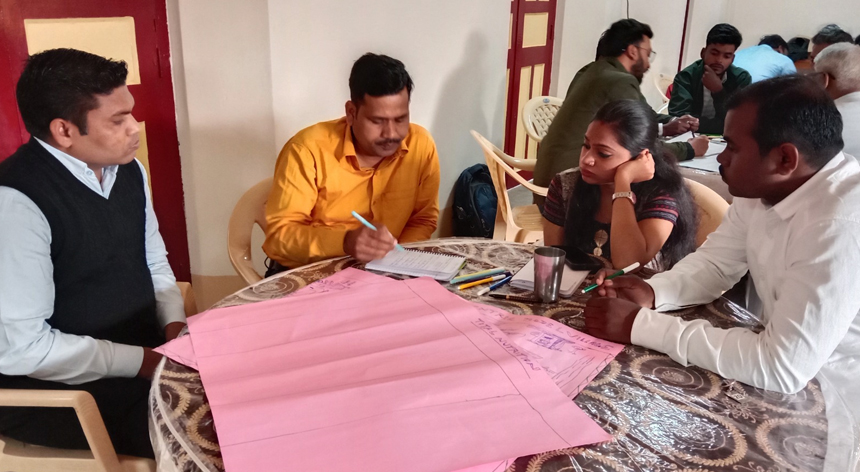

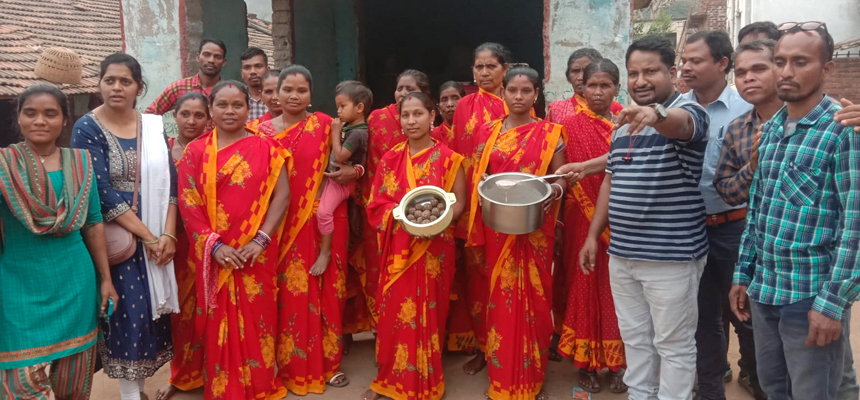
Nutrition and Food Security partners prepared nutrition-centric plans for villages
Nutrition and Food Security partners from Bihar and Odisha prepared the nutrition-centric plan including a need assessment, action plan, timeline, strategies, working place, and resource sharing to address the food and nutrition security of the community. Poverty reduction and food security are one of the main objectives of Global Program India which also contributes towards SDG2. The programme aims towards improving food security by intensive targeting by means of improved access to government programmes.




